Green Finance: The Rise of Climate-Conscious Investing
Green finance is transforming global markets shifting capital toward sustainability, climate-conscious investments, and ESG-driven growth. From green bonds to carbon markets, explore how finance is becoming a force for planetary and economic resilience.

In a world increasingly impacted by climate change, environmental degradation, and resource scarcity, finance is evolving from a purely profit-driven discipline into a powerful force for sustainability. The concept of "Green Finance" has emerged as a critical tool in addressing global environmental challenges while generating long-term economic value. This movement is not just a passing trend—it's a fundamental shift in how capital is allocated across markets and industries.
What is Green Finance?
Green finance refers to structured financial activities that are designed to deliver environmental benefits in the broader context of sustainable development. This includes investments in renewable energy, pollution reduction, sustainable agriculture, biodiversity conservation, and climate-resilient infrastructure.
More broadly, green finance supports projects and initiatives that contribute positively to the environment and climate, while also creating financial returns for investors. It encompasses a wide range of instruments, including green bonds, ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) funds, sustainability-linked loans, and carbon markets.
Why Green Finance Matters
Climate change presents an existential threat to the global economy. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and ecosystem collapse are already disrupting supply chains, damaging infrastructure, and displacing communities. The financial costs are staggering and growing every year.
Green finance is a strategic response to these risks. By channeling capital into climate-friendly projects and penalizing environmentally harmful activities, green finance incentivizes corporate and governmental accountability. It provides investors a way to align their portfolios with climate goals while mitigating long-term financial risks.
ESG Funds: Investing with Purpose
One of the most visible and rapidly growing segments of green finance is ESG investing. ESG funds are investment vehicles that consider environmental, social, and governance factors alongside traditional financial metrics when selecting securities.

Environmental Criteria
These look at a company’s energy use, waste, pollution, natural resource conservation, and treatment of animals. They also evaluate any environmental risks the company might face and how it manages those risks.
Social Criteria
This examines how it manages relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, and the communities where it operates. It includes diversity and inclusion practices, labor standards, and community engagement.
Governance Criteria
This deals with a company’s leadership, executive pay, audits, internal controls, and shareholder rights.
Investors are increasingly directing funds toward companies that score high on ESG metrics. From millennials to institutional investors, the demand for sustainable investing is growing at a pace that is reshaping asset management. Companies, in turn, are adapting by integrating ESG principles into their operations to attract investment and improve market valuation.
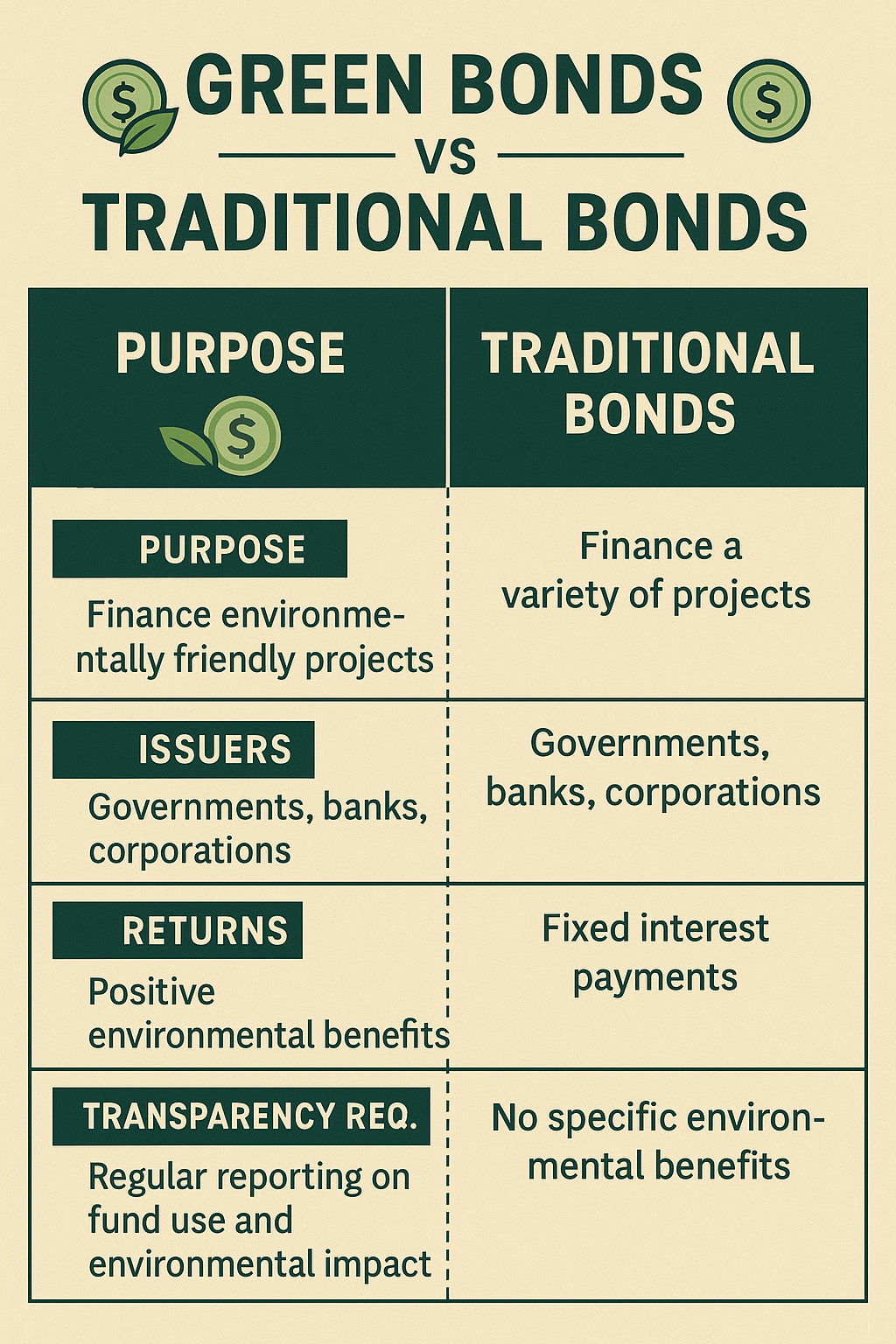
The Surge of Green Bonds
Green bonds are debt securities issued to finance or refinance environmentally beneficial projects. Governments, municipalities, banks, and corporations can all issue green bonds, provided the proceeds are earmarked for green projects.
How Green Bonds Work
Just like traditional bonds, green bonds pay interest over a fixed period and return the principal amount at maturity. What differentiates them is the mandatory use of proceeds for green initiatives like renewable energy installations, clean transportation, or sustainable water management.
Benefits of Green Bonds
- Transparency: Issuers are usually required to provide regular updates on the use of funds and environmental impact.
- Investor Attraction: Green bonds appeal to environmentally conscious investors and those with ESG mandates.
- Reputational Boost: Issuing green bonds signals commitment to sustainability, which can enhance a company’s brand image.
The green bond market has seen exponential growth in recent years. As both public and private sectors strive to meet climate goals, these instruments are expected to play an even larger role in the financial ecosystem.
Carbon Markets: Pricing Pollution
Carbon markets are mechanisms that allow for the buying and selling of carbon emission allowances or credits. These markets essentially put a price on carbon emissions, creating a financial incentive for companies to reduce their carbon footprint.
Cap-and-Trade Systems
In a cap-and-trade system, governments set a cap on the total amount of greenhouse gases that can be emitted by all participating entities. Companies receive or purchase emission allowances and can trade them with others. If they emit less, they can sell their excess; if they emit more, they must buy credits.
Voluntary Carbon Markets
Outside regulated systems, voluntary carbon markets allow companies and individuals to purchase carbon offsets to compensate for their emissions. These offsets fund projects like forest conservation, renewable energy, and methane capture.
Challenges in Carbon Markets
Despite their promise, carbon markets face issues related to verification, double-counting, and inconsistent regulation. Ensuring that credits represent real, additional, and permanent emission reductions is key to maintaining integrity.
Corporate Sustainability and Reporting
Green finance has also pushed companies toward greater transparency. ESG reporting is now a standard requirement for many publicly traded firms. Regulatory bodies and stock exchanges are introducing mandatory sustainability disclosures, ensuring that investors have access to information on climate-related risks and opportunities.
In India, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has implemented the Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) framework. In the U.S., the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is also moving toward climate-related disclosures.
Fintech and Green Finance
Technology is accelerating the adoption of green finance. Fintech platforms are making it easier for individuals to invest in ESG funds, buy green bonds, or participate in carbon offset programs. Blockchain technology is being explored for transparent tracking of carbon credits. Artificial intelligence is being used to analyze ESG data and identify sustainable investment opportunities.
Digital finance, when aligned with environmental objectives, creates powerful synergies. Crowdfunding for green projects, peer-to-peer lending for clean energy solutions, and digital wallets that calculate carbon footprints are just a few innovations in this space.
Government Initiatives and Policy Support
Governments around the world are increasingly supporting green finance through policy incentives, regulatory frameworks, and public funding.
In India, the government has launched the Sovereign Green Bond program to fund public-sector green initiatives. In the U.S., the Inflation Reduction Act includes provisions for climate financing, renewable energy incentives, and electric vehicle infrastructure.
Globally, frameworks like the EU Taxonomy and the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a shared language and metrics for evaluating green finance initiatives.
The Challenges Ahead
While the momentum is strong, green finance still faces multiple hurdles:
- Greenwashing: The risk that companies exaggerate or falsely claim environmental benefits to attract ESG investment.
- Standardization: Lack of universal definitions and metrics for what constitutes "green" makes comparison and assessment difficult.
- Accessibility: Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) often struggle to access green finance due to complex application processes or lack of awareness.
- Market Volatility: Economic downturns can deprioritize sustainability in favor of short-term returns.
Addressing these issues requires stronger regulatory oversight, better ESG rating systems, improved disclosure standards, and enhanced investor education.
The Road Ahead: Integrating Sustainability into the Financial Core
The ultimate goal of green finance is not to create a parallel financial system but to integrate sustainability into the core of all financial decision-making. This includes:
- Embedding ESG risk assessments into credit ratings and investment analysis.
- Encouraging banks to align loan portfolios with climate goals.
- Promoting green financial literacy among consumers and investors.
- Creating public-private partnerships to finance large-scale green infrastructure.
Conclusion
Green finance is not merely a trend; it's an essential evolution of the financial system in the face of environmental urgency. As climate challenges intensify, the fusion of finance and sustainability will play a decisive role in determining the world’s trajectory.
Investors, policymakers, corporations, and consumers all have a role to play. Whether it’s through ESG investing, buying green bonds, participating in carbon markets, or demanding transparency, each action contributes to a greener, more resilient future.
The rise of climate-conscious investing is not just about mitigating risk—it’s about seizing the opportunity to shape a world where prosperity and the planet coexist. In this financial revolution, sustainability is the new benchmark of value, and green finance is its guiding force.
For more legal exposes and truth-behind-glamour stories, subscribe to AllegedlyNewsNetwork.com




