Nvidia Surges to the Top: How the AI Chip Titan Became the World's Most Valuable Company Again
Nvidia becomes the world’s most valuable company again, surpassing Apple and Microsoft, driven by AI chip dominance, strategic leadership, and global demand.

SANTA CLARA, June 27, 2025
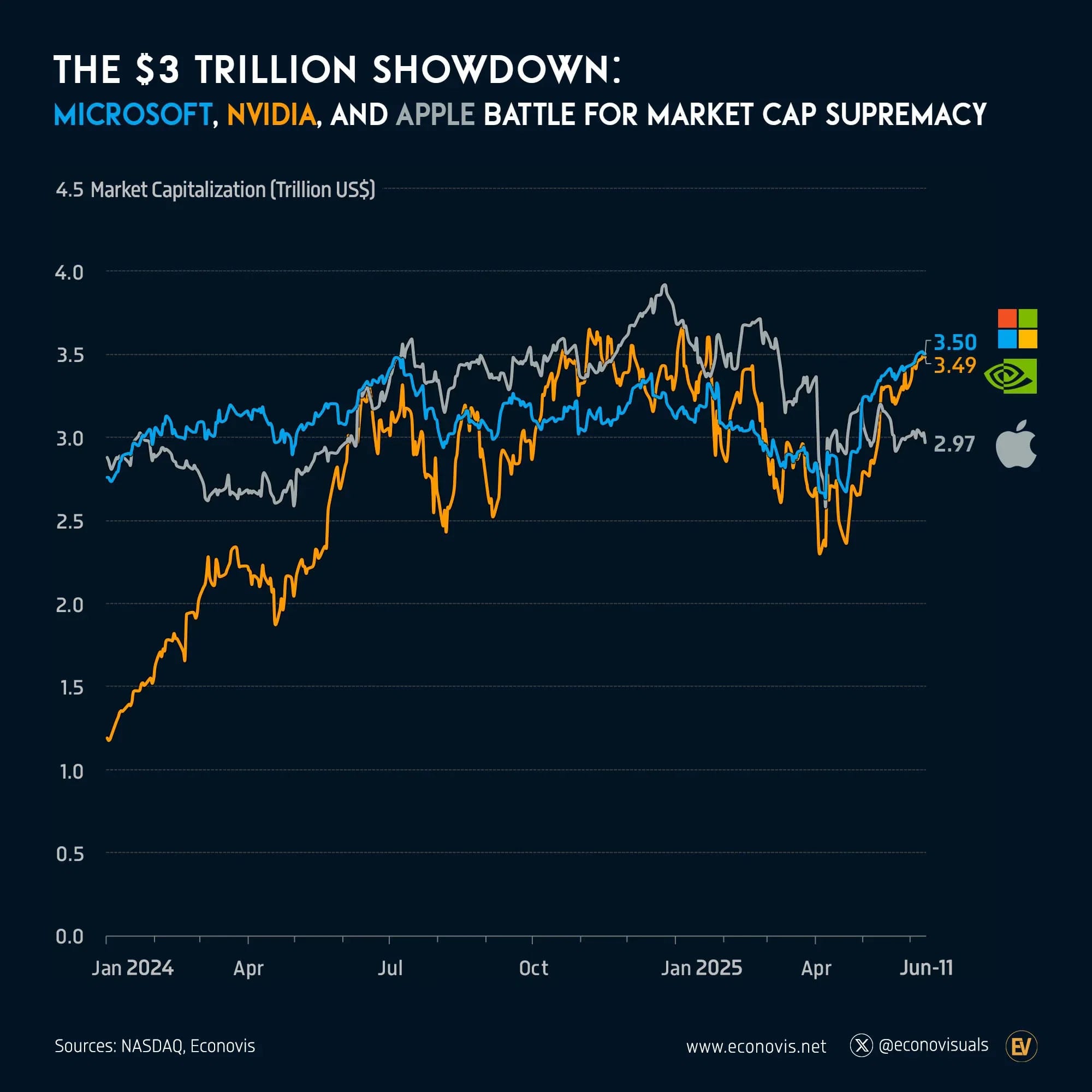
In a moment that will be etched in Silicon Valley history, Nvidia has reclaimed the title of the world’s most valuable publicly traded company. It surpassed Apple and Microsoft, reaching a market capitalization of over $3.77 trillion. This achievement is more than just success for one company; it symbolizes a changing technological era driven by artificial intelligence, data infrastructure, and geopolitical tech rivalries.
This blog will examine Nvidia’s rise, the technology that supports it, economic and political consequences, and what this change means for the future of the global economy.
The AI Hardware Revolution: Redefining the Semiconductor Landscape
Central to Nvidia’s valuation is its clear leadership in AI processing hardware, particularly GPUs (graphics processing units) and AI-focused chips like Blackwell, Hopper, and the upcoming Vera Rubin.
The Tech That Powers the Surge
- H100 & B200 (Blackwell): These chips have become essential in training large AI models, including OpenAI’s GPT-5, Google Gemini, and Meta’s LLaMA. With unmatched computing power per watt, Nvidia leads in the AI datacenter market.
- CUDA Ecosystem: Nvidia’s proprietary software stack allows developers to create applications specifically for its hardware. This creates an environment that fosters developer loyalty and dependence on the platform.
- Vera Rubin Architecture (2025–2026): Scheduled for release in Q4, this next-generation platform is expected to double AI inference speeds while improving energy efficiency, a critical factor as global data centers deal with increasing energy demands.
“Accelerated computing and generative AI have reached a tipping point. Demand is rising across every industry.” — Jensen Huang, Nvidia CEO
From $1 Trillion to $3.77 Trillion: Tracking the Ascent
In early 2023, Nvidia became the first chipmaker to achieve a $1 trillion valuation. By mid-2025, it broke records:
- April 2025: Share price dropped to about $94 due to broader tech market corrections.
- June 2025: Shares climbed past $155, peaking at $156.99, taking Nvidia’s market cap beyond Microsoft ($3.66T) and Apple ($3.01T).
This shift goes beyond numbers; it reflects changing priorities in the global tech economy. Nvidia’s tools are not just improving gaming; they are powering language models, autonomous vehicles, medical simulations, defense analytics, and quantum experiments.
Wall Street Response
- Goldman Sachs raised Nvidia’s 12-month target to $250, pointing to growing AI demand and global chip shortages.
- Bernstein stated that “Nvidia now supports the 21st-century internet economy,” referring to it as the “arms dealer in the AI war.”
Jensen Huang: Leader of a Technological Renaissance
It is rare for a CEO to become synonymous with a technological shift of a generation, but Jensen Huang has achieved that.
His background in electrical engineering (Oregon State) and computer science (Stanford) provides him with technical credibility.
Huang has led Nvidia through the 2008 crisis, the crypto-GPU era, and now AI, making the company one of the most flexible tech firms globally.
At Nvidia’s 2025 shareholder meeting, Huang projected a multitrillion-dollar opportunity in autonomous robotics, synthetic biology, and national AI infrastructure.
His visionary reputation places him among elite figures, often compared to Steve Jobs and Elon Musk, but with a uniquely “quiet genius” leadership style that combines bold research investments with long-term planning.
International Factors: Chip Wars, Global Demand & Trade Controls
The AI boom is not happening in isolation. Nvidia’s rise is linked to geopolitics, supply chains, and semiconductor policy.
China and Export Restrictions
- U.S. restrictions have banned Nvidia’s high-end AI chips (like A100, H100, and now B200) from being sold in China.
- Nvidia responded with “compliant” chips like H20, L20, and L2, which offer slightly lower performance for legal export.
“You can't have it both ways,” Huang said at a June tech conference. “If you cut off supply, you foster domestic innovation. China will build its own ecosystem faster than you think.”
Global Demand
From India’s National AI Cloud to the EU’s Sovereign GPU Infrastructure, every region is investing in computing power. Nvidia remains the top provider for:
- AI supercomputers
- Smart city networks
- 5G core inference hardware
- Medical AI diagnostics
Nvidia’s partnerships with Samsung, TSMC, and ASML help it navigate trade uncertainties better than its competitors.
Sector Impacts: How Nvidia Is Reshaping Global Markets
The Nvidia Effect on Competitors
- AMD lags in high-end AI but remains strong in consumer graphics.
- Intel has shifted to its Gaudi AI series but faces challenges with developer acceptance.
- Qualcomm is targeting edge AI (phones, cars), an area Nvidia is also exploring.
- TSMC, while not a direct competitor, benefits from Nvidia’s success as a foundry partner.
Consolidation and Acquisition Watch
Rumors suggest Nvidia is considering:
- A quantum hardware startup (like Rigetti or PsiQuantum)
- An AI chip design firm (possibly Tenstorrent or Graphcore)
Such moves would strengthen its dominance from silicon to systems.
Beyond Chips: Software, Platforms & Omniverse
Nvidia is shifting from being just a chipmaker to a platform company.
Omniverse
Their digital twin simulation platform, Omniverse, is used in various applications, from optimizing BMW factories to testing NASA space missions. It is rapidly growing as industries model real-world systems in AI-enhanced simulations.
Healthcare, Robotics & Beyond
- Clara AI powers cancer diagnostics and genomics.
- Isaac SDK is used in Amazon warehouses for robotics automation.
- Jetson platforms are found in drones, satellites, and surveillance systems worldwide.
Risks: What Could Go Wrong?
Despite its success, Nvidia faces systemic and company-specific risks:
- Regulatory risk: Increasing scrutiny of “AI monopolies” and potential antitrust actions.
- Geopolitical instability: If tensions between Taiwan and China rise, Nvidia’s foundry network could be threatened.
- New challengers: Google’s TPUs, Amazon’s Trainium, and Meta’s custom silicon pose long-term risks.
- Market volatility: A bubble in AI stocks or a recession could lead to a temporary drop in demand.
Still, Nvidia is diversifying its revenue, managing geopolitical risks, and reinvesting over 20% of its profits into research and development. This is a notably high rate for large companies.
What Happens Next?
The trillion-dollar question: Can Nvidia stay #1?
Short-term indicators suggest growth:
- Strong fiscal results (Q2 2025: $26B revenue; 73% gross margins).
- Demand for AI chips is expected to triple by 2027.
- Nvidia’s new product lineup includes Blackwell Ultra, Vera Rubin, and a rumored dedicated quantum accelerator.
Long-term, Nvidia will need to:
- Keep evolving its architecture to outpace custom chips.
- Increase software-as-a-service revenue.
- Expand globally in emerging AI markets (like Indonesia, Brazil, and MENA).
The Nvidia Era: Power, Chips, and the AI Race
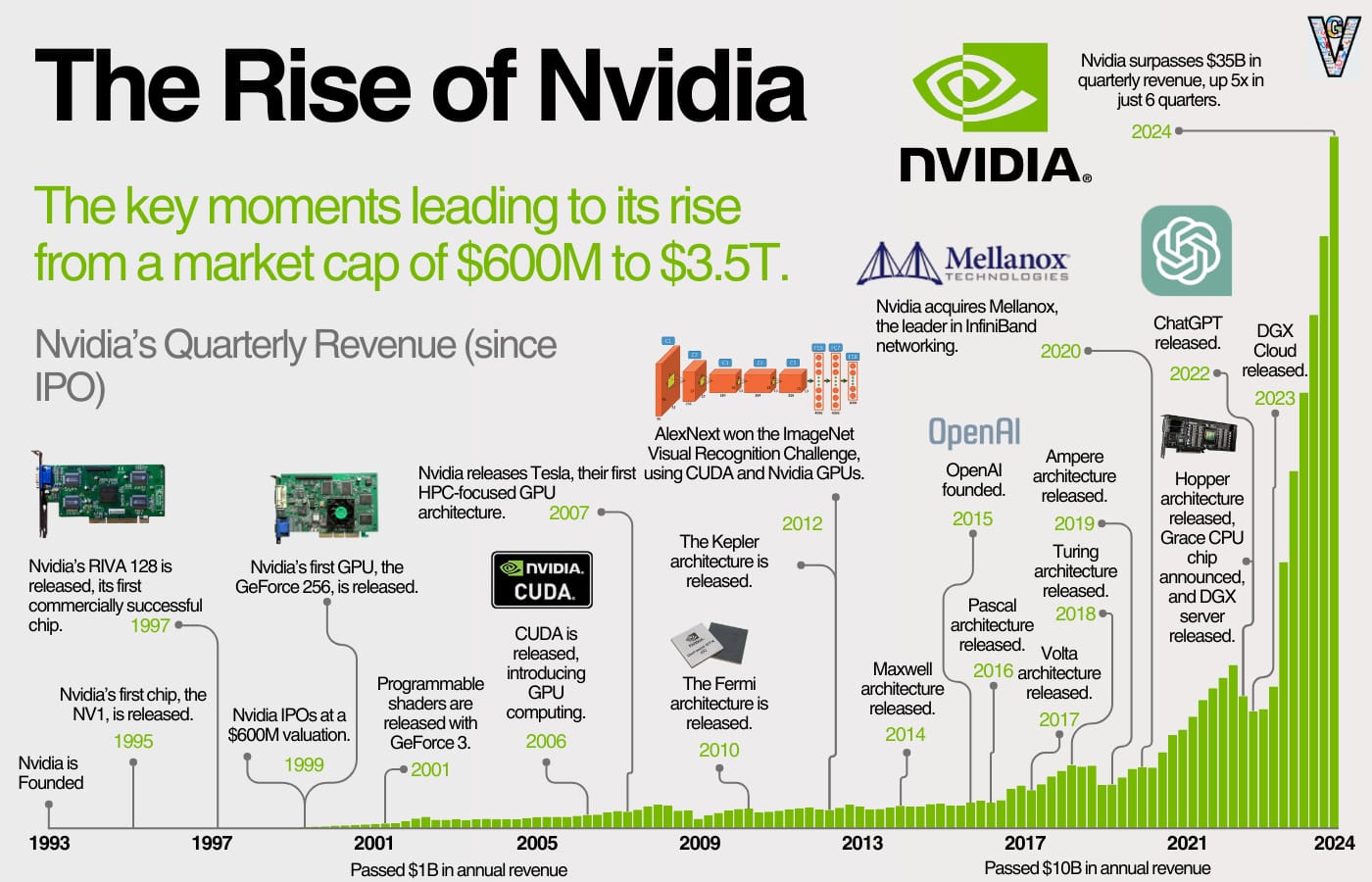
From a gaming card company in the 1990s to a leader in the AI era, Nvidia’s journey is one of change, innovation, and timing. Its story extends beyond technology; it involves the future of work, governance, defense, and human thinking itself.
Jensen Huang has stated, “We’re no longer a graphics company—we’re an AI factory.” This evolution has paid off. However, in the race for computing power, being first doesn’t always guarantee lasting success. The world will be watching to see if Nvidia can translate its current success into a lasting empire or if another giant is waiting to step in.
Your Turn: Is Nvidia Shaping the Future—or Owning It?
Do you believe Nvidia's rapid dominance in AI infrastructure is sustainable, or could it lead to dangerous centralization of power in the tech world? What checks should be in place? Is Nvidia’s lead in AI a result of visionary engineering, or is it paving the way for monopolistic control over the most critical resource of tomorrow—intelligence infrastructure?
Sources
- Market data and financial updates: Yahoo Finance (Nvidia stock quote, June 27, 2025); Nasdaq listing data; Nvidia Q2 2025 Earnings Report.
- News analysis: Reuters (AI boom and stock upgrade reports), Bloomberg (valuation tracking), MarketWatch (chip sector rally), Business Insider (shareholder meeting coverage), Financial Times (export control and geopolitical impact).
- Industry background and company profile: Wikipedia (Nvidia corporate history), Times of India (Nvidia–Microsoft–Apple market value updates), Investopedia (technical analysis of Nvidia breakout levels).
- Official statements and leadership quotes: Jensen Huang (shareholder address, June 2025); Nvidia press releases and investor calls.
- Media Insights: Econovis / NASDAQ – Market Cap Comparison Chart, Visual Capitalist – The Rise of Nvidia, OpenAI DALL·E.
- Public interest and sentiment: Google Trends (search data for Nvidia and AI chips); Reddit (r/investing and r/technology threads on Nvidia stock momentum).




