The Quantum Internet Is Coming And It’s Not Just for Scientists
The quantum internet promises unhackable communication, instant data teleportation, and unprecedented scientific collaboration. Once the domain of labs, it’s on track to transform banking, healthcare, climate research, and entertainment reshaping how the world connects.

The Future is Flickering Into View
It sounds like science fiction: an internet that can send unhackable messages, teleport data instantly between cities, and make today’s broadband look like a dusty telegraph line. But in labs from Delft to Beijing, engineers are piecing together the building blocks of the quantum internet a network that doesn’t just transmit bits (1s and 0s) but qubits, particles entangled in a strange quantum dance.
And here’s the twist: this isn’t just for physicists in white coats. Over the next two decades, quantum networking could shape everything from global finance to personal privacy, climate modeling to immersive entertainment. In the same way nobody in 1994 could predict TikTok or Uber, the true potential of a quantum internet lies in applications we haven’t yet imagined.
Quantum 101 — Why It’s Different
Before we dive into the wild possibilities, it’s worth asking: what makes the quantum internet different from the one you’re using to read this right now?
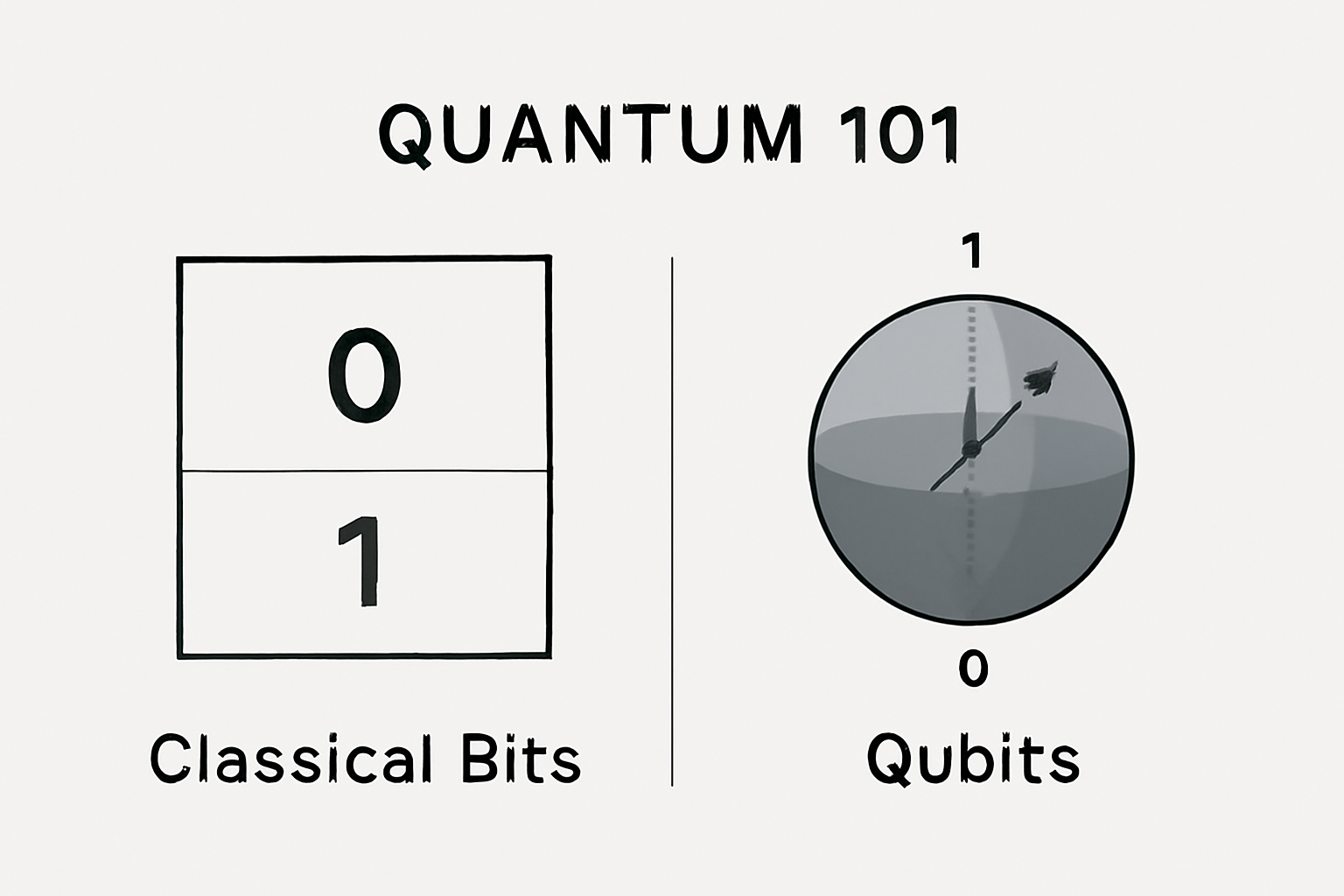
Bits vs Qubits
- Classical Internet: Data is sent in binary form ones and zeros as electrical signals or light pulses down fiber-optic cables.
- Quantum Internet: Data is encoded in qubits, which can be 0, 1, or both at the same time thanks to quantum superposition.
Entanglement: The Magic Trick
When two particles are entangled, a change to one instantly affects the other — no matter the distance between them. This isn’t metaphorical; it’s been tested in experiments spanning hundreds of kilometers. In networking terms, it means you can share states between devices in a way that’s impossible to intercept without detection.
Why Hackers Hate It
Quantum communication can reveal eavesdroppers instantly, because measuring a qubit changes it. This makes certain types of spying or hacking physically impossible a godsend for governments, banks, and privacy-conscious citizens.
The Quiet Race to Build It
In a few research hubs, the pieces are falling into place:
- China: Demonstrated a 1,200-kilometer quantum-secure communication link between Beijing and Shanghai, and launched the Micius satellite for space-based quantum key distribution.
- European Union: Building a “Quantum Internet Alliance” to connect labs across the continent with quantum repeaters.
- United States: The Department of Energy has unveiled a national blueprint for a quantum network spanning major cities.
- Japan, Canada, Australia: Running hybrid experiments that link quantum systems to existing fiber networks.
It’s not a single race it’s more like a planetary relay, with researchers in different time zones pushing each other forward.
What You Could Do on a Quantum Internet
For many, the word “quantum” feels distant, like a puzzle in a physics textbook. But here’s where it gets personal.
1. Banking in a World Without Fraud
Imagine logging into your bank account without a password, PIN, or even two-factor authentication because the communication channel itself is unbreakable. Quantum key distribution (QKD) could make data theft impossible for any realistic attacker, even a superpowered AI with a million years to try.
For high-frequency traders, quantum links could reduce delays to the absolute physical limit the speed of light giving new meaning to “real-time” markets.
2. Medical Research on Steroids
Today’s drug discovery involves sifting through astronomical combinations of molecules. Quantum networks could connect quantum computers in different locations, pooling their processing power to simulate complex biological systems. Instead of years to find a potential cancer treatment, it could take months or even weeks.
And with secure quantum links, hospitals could share anonymized patient data without fear of leaks, enabling global-scale health analytics in real time.
3. Climate Modeling That’s Actually Useful
Predicting Earth’s climate involves processing trillions of variables something classical supercomputers struggle to do accurately beyond a few decades. A networked quantum computing system could run models with far greater precision, helping cities prepare for floods, farmers plan for droughts, and governments respond to disasters before they spiral.
4. Entertainment That Feels Real
Picture a fully immersive multiplayer VR game where the physics of the virtual world are so accurate they obey quantum mechanics themselves because they’re running on linked quantum processors.
The latency? Practically zero.
The realism? Mind-bending.
It’s not just better graphics it’s a new medium entirely.
5. The Personal Privacy Renaissance
In an era where every click is tracked, quantum networks could bring privacy back to everyday life.
- Private messaging apps would be mathematically immune to wiretaps.
- Voting systems could be verifiable yet anonymous.
- Your smart devices could share data securely without bleeding your personal information to third parties.
Why It’s Not Here Yet
If all this sounds amazing, you might be wondering why we’re still squinting at grainy Zoom calls instead of teleporting ultra-secure holograms.
The problem is that quantum states are fragile. A qubit can lose its delicate superposition due to interference, heat, or even cosmic rays. Over long distances, this “decoherence” kills the signal.
To fix this, researchers are working on:
- Quantum Repeaters: Devices that extend the range of entanglement without breaking it.
- Error Correction: Algorithms that detect and fix quantum state errors in real time.
- Hybrid Links: Combining classical and quantum channels for stability.
The challenge isn’t just engineering — it’s infrastructure. The quantum internet may require new cables, satellites, and protocols, much like the early days of the classical web.
From Lab Curiosity to Public Utility
The path to mainstream quantum networking will likely follow three phases:
- Phase One: Specialized Use (2025–2035)
Governments, militaries, and banks use it for critical communications. Quantum-safe messaging apps and file transfers become niche commercial services. - Phase Two: Hybrid Integration (2035–2045)
Quantum repeaters connect cities; data centers link quantum processors for scientific research. Some consumer products, like medical devices or VR platforms, begin using quantum-secured backbones.
Phase Three: Public Quantum Web (2045–2055)
The quantum internet becomes as common as Wi-Fi, enabling applications that don’t even exist today just as social media and cloud computing were unforeseen in 1990.
The Social Impact Not All Roses
A network this powerful also comes with risks:
- Geopolitical Tensions: The country that controls the first large-scale quantum network could hold massive strategic power.
- Economic Inequality: Wealthy nations and corporations may monopolize early benefits, widening the tech gap.
- Security Paradox: While quantum communication can be unbreakable, quantum computers could still break much of today’s encryption, forcing a global scramble to upgrade security.
And, as with all technology, there’s the cultural shock factor societies may not be ready for the transparency and speed quantum networks could enable.
The Day You’ll Notice It
For most people, the quantum internet won’t arrive with a fanfare. One day, your bank app might simply say “Quantum Secure Channel Established” when you log in. Your video calls will stop glitching. Your smart home devices will talk to each other without leaking your private data.
It will be woven into daily life quietly much like fiber optics, GPS, or the undersea cables that already power our world.
The difference is that the quantum internet could redefine what’s possible, not just what’s convenient.
Final Word: The Invisible Revolution
The quantum internet is more than just “faster Wi-Fi.” It’s a whole new layer of reality, one where information behaves according to the strange and beautiful rules of quantum mechanics.
For now, it’s a patchwork of experiments and prototypes. But so was the classical internet in 1973. The difference this time? The stakes are higher, the potential broader, and the race much faster.
When it arrives whether in a decade or a generation it won’t just connect computers. It will connect possibilities we can barely imagine.
The quantum age is coming. And it won’t just belong to scientists. It will belong to all of us.
Sources:
Research & Science
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) - Quantum networking initiatives
- Delft University of Technology — Quantum Internet Alliance project details
- Nature & Science journals — Peer-reviewed studies on quantum communication
Government & Policy
- U.S. Department of Energy — Quantum Internet Blueprint
- European Commission — Quantum Communication Infrastructure plans
- Chinese Academy of Sciences — Micius satellite experiments




